IV. Whom For?
4.1. Disabled and Disability
4.1.5. Hardware and Software Disability?
On the Internet, hardware, software, or the type of connection used can also be a disability to access the content of a website.
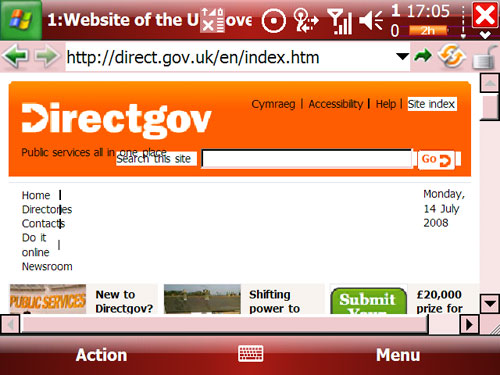
Figure 4.12: DirectGov website seen on a PDA.
Note: The screenshot was made on a HTC PDA, reference: Advantage X7500, using the Windows Mobile® 5.0 Pocket PC Phone Edition operating system. As can be seen, some texts are overlapping others.
Indeed, depending on the device used to browse the web, some website may become inaccessible. This has become particularly true with the development of mobile technologies (mobile phones, PDAs...) that allow their user to browse the web; but this also concerns older computers. The major difficulty encountered when browsing the Internet with mobile device is the size of the screen and the slow and expensive internet connection. If recent smartphone such as the iPhone are offering high speed connection, it is not the case of most mobile phones that generally offer a speed equivalent to the one of a dial-up modem. It is also important to note that many mobile phones are not able to handle cookies or JavaScript, which can cause trouble accessing password protected areas that use cookies to control login for example.
Moreover, the software chosen to browse the web can also be problematic. Indeed, as seen in section 2.2.3. Study Conclusions 2% of the Internet users still use very old web browsers, such as Internet explorer 5 or Netscape. These older browsers do not interpret HTML and CSS perfectly, which cause accessibility problems.
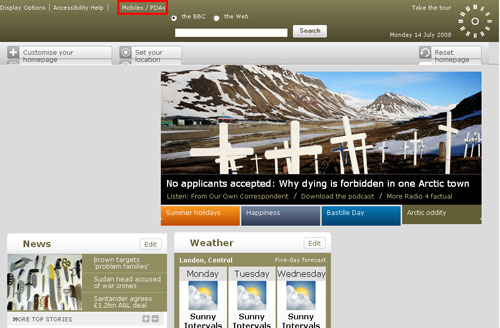
Figure 4.13: Screenshot of the BBC.co.uk homepage viewed in Internet Explorer 5
Note: As can be seen on the image, the layout of the website is severely deformed, some important links became difficult to read and some others are even non clickable anymore.
Finally, the Internet Connectivity study released by the Office for National Statistics in march 2008 shows that 8.4% of Internet user in the UK still use a dial-up connection (Office for National Statistics, 2008). The reason people do subscribe to a broadband connection is generally because this type of connection is not available in their area of living, including much of rural Scotland. Among the broadband subscribers, 43.1% have a connection speed inferior to 2Mbps; 50.5% have a connection speed comprised between 2 and 8 Mbps; and 6.4% have a connection speed superior to 8Mbps (Office for National Statistics, 2008). A slow internet connection can damage the Internet user experience, especially if the website they want to browse is particularly heavy, or need them to download extra plug-ins (See Table 4.3).
| Time needed for loading | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Website | Weight (Kb) | 56Kbps | 128Kbps | T1 – 1.44Mbps |
| Google.com | 11 | 2.7 s | 1 s | 0.5 s |
| BBC.co.uk | 211.5 | 45 s | 16 s | 4 s |
| GetOnBoardNow.org | 1100 | 3 min 44 s | 1 min 12 s | 11 s |
It is thus important in the development of a website, to make sure that no user will be excluded from browsing it because he doesn’t use the same configuration as the developers do. Old browser can be accommodated by specifying a special CSS style sheet for them with the use of conditional comments:
<!--[if lte IE 6]>
This HTML code will only be interpreted by Internet Explorer 6 and its previous versions
<![endif]-->
It is also important to make sure that the weight of web page is reasonable, that it doesn’t contain too many very heavy picture or animations.